Miscarriage
Contents
When to Contact a Medical Professional
General Information
A miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a fetus before the 20th week of pregnancy. (Pregnancy losses after the 20th week are called preterm deliveries.)
A miscarriage may also be called a "spontaneous abortion." This refers to naturally occurring events, not to medical abortions or surgical abortions.
Other terms for the early loss of pregnancy include:
- Complete abortion: All of the products (tissue) of conception leave the body
- Incomplete abortion: Only some of the products of conception leave the body
- Inevitable abortion: Symptoms cannot be stopped and a miscarriage will happen
- Infected (septic) abortion: The lining of the womb (uterus) and any remaining products of conception become infected
- Missed abortion: The pregnancy is lost and the products of conception do not leave the body
The doctor may also use the term threatened miscarriage. The symptoms of this condition, abdominal cramps with or without vaginal bleeding, are a sign that a miscarriage may occur.
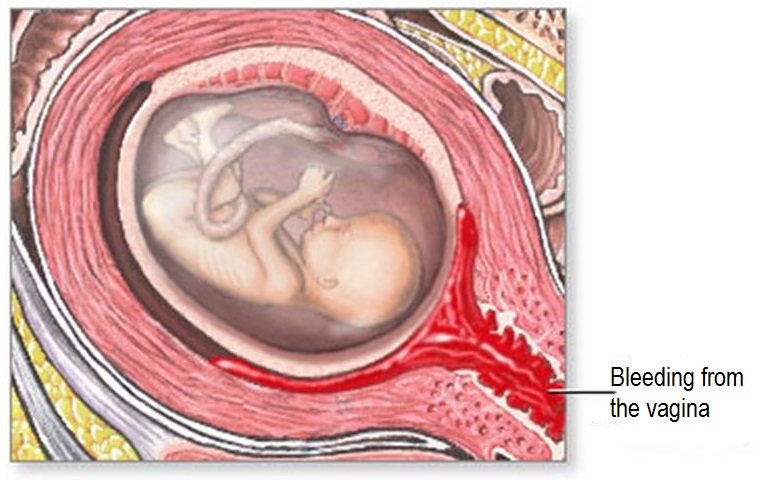
A threatened miscarriage or spontaneous abortion occurs in approximately 10% of pregnancies between 7 and 12 weeks of gestation. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding, abdominal cramps, and low back pain.
Causes
Most miscarriages are caused by chromosome problems that make it impossible for the baby to develop. Usually, these problems are not related to the mother or father's genes.
Other possible causes of miscarriage include:
- Drug and alcohol abuse
- Exposure to environmental toxins
- Hormone problems
- Infection
- Obesity
- Physical problems with the mother's reproductive organs
- Problem with the body's immune response
- Serious body-wide (systemic) diseases in the mother (such as uncontrolled diabetes)
- Smoking
Around half of all fertilized eggs die and are lost (aborted) spontaneously, usually before the woman knows she is pregnant. Among women who know they are pregnant, the miscarriage rate is about 15-20%. Most miscarriages occur during the first 7 weeks of pregnancy. The rate of miscarriage drops after the baby's heart beat is detected.
The risk of miscarriage is higher in women:
- Who are older, with increases beginning by age 30, becoming greater between 35 and 40, and highest after 40.
- Who have had previous miscarriages.
Symptoms
Possible symptoms include:
- Low back pain or abdominal pain that is dull, sharp, or cramping
- Tissue or clot-like material that passes from the vagina
- Vaginal bleeding, with or without abdominal cramps
Exams and Tests
During a pelvic exam, your health care provider may see the cervix has opened (dilated) or thinned out (effacement).
Abdominal or vaginal ultrasound may be done to check the baby's development, heart beat, and amount of bleeding.
The following blood tests may be performed:
- Blood type (if you have an Rh-negative blood type, you would require a treatment with Rh-immune globulin. See: Rh incompatibility)
- Complete blood count (CBC) to determine how much blood has been lost
- HCG (qualitative) to confirm pregnancy
- HCG (quantitative) done every several days or weeks
- WBC and differential to rule out infection
Treatment
When a miscarriage occurs, the tissue passed from the vagina should be examined. This is done to determine if it was a normal placenta or a hydatidiform mole. It is also important to determine whether any pregnancy tissue remains in the uterus.
If the pregnancy tissue does not naturally leave the body, the woman may be closely watched for up to 2 weeks. Surgery (D and C) or medication (such as misoprostol) may be needed to remove the remaining contents from the womb.
After treatment, the woman usually resumes her normal menstrual cycle within 4 - 6 weeks. Any further vaginal bleeding should be carefully monitored. It is often possible to become pregnant immediately. It is recommended that women wait one normal menstrual cycle before trying to become pregnant again.
Possible Complications
Complications of a complete miscarriage are rare.
An infected abortion may occur if any tissue from the placenta or fetus remains in the uterus after the miscarriage. Symptoms of an infection include fever, vaginal bleeding that does not stop, cramping, and a foul-smelling vaginal discharge. Infections can be serious and require immediate medical attention.
Women who lose a baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy receive different medical care. This is called premature delivery or fetal demise and requires immediate medical attention.
After a miscarriage, mothers and their partners may feel sad. This is normal. If your feelings of sadness do not go away or get worse, seek advice from family and friends as well as your health care provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if vaginal bleeding with or without cramping occurs during pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you are pregnant and notice tissue or clot-like material that passes through the vagina. The material should be collected and brought to the health care provider for examination.
Prevention
Early, comprehensive prenatal care is the best prevention for complications of pregnancy, such as miscarriage.
Miscarriages that are caused by body-wide (systemic) diseases can be prevented by detecting and treating the disease before pregnancy occurs.
Miscarriages are also less likely if you avoid things that are harmful to your pregnancy. These include x-rays, recreational drugs, alcohol, high caffeine intake, and infectious diseases.
When a mother's body has difficulty keeping a pregnancy, signs such as slight vaginal bleeding may occur. This means there is a possibility of miscarriage. But it does not mean one will definitely occur. A pregnant woman who develops any signs or symptoms of threatened miscarriage should contact her prenatal provider immediately.

