Trigeminal neuralgia
Contents
Trigeminal neuralgia is a nerve disorder that causes a stabbing or electric-shock-like pain in parts of the face.
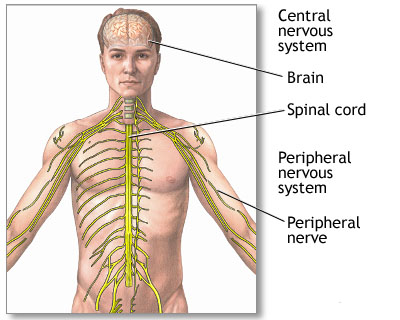
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
The pain of trigeminal neuralgia comes from the trigeminal nerve. This nerve carries the feelings of touch and pain from the face, eyes, sinuses, and mouth to the brain.
The condition usually affects adults, but it may affect anyone at any age. Trigeminal neuralgia may be part of the normal aging process.
Trigeminal neuralgia may be caused by:
-
Multiple sclerosis
-
Pressure on the trigeminal nerve from a swollen blood vessel or tumor
Often, no cause is found.
Doctors are more likely to find a cause in a person who is younger than age 40.
-
Very painful, sharp electric-like spasms that usually last a few seconds or minutes, but can become constant
-
Pain is usually only on one side of the face, often around the eye, cheek, and lower part of the face
-
Pain may be triggered by touch or sounds
-
Painful attacks of trigeminal neuralgia can be triggered by common, everyday activities, such as:
-
Brushing teeth
-
Chewing
-
Drinking
-
Eating
-
Lightly touching the face
-
Shaving
A brain and nervous system (neurologic) examination is usually normal.
Tests that are done to look for the cause of the problem include:
-
Blood tests
-
MRI of the head
-
Trigeminal reflex testing
Your primary care physician, a neurologist, or a pain specialist may be involved in your care.
Certain medicines sometimes help reduce pain and the rate of attacks. These medicines include:
-
Anti-seizure drugs (carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, phenytoin, valproate, and pregabalin)
-
Muscle relaxants (baclofen, clonazepam)
-
Tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, or carbamazepine)
Some patients may need surgery to relieve pressure on the nerve. Techniques include:
-
Cutting or destroying part of the trigeminal nerve
-
Destroying the trigeminal nerve with a needle or probe placed through the skin using radiofrequency ablation or an injection of glycerol
-
Electrostimulation
-
Percutaneous balloon microcompression
-
Removal of the tumor (when a tumor is the cause)
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma knife)
-
Surgery to remove a blood vessel that is putting pressure on the trigeminal nerve (called microvascular decompression, or MVD)
How well you do depends on the cause of the problem. If there is no disease causing the problem, treatment can provide at least some relief.
However, the pain may become constant and severe in some patients.
Tic douloureux
Source: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000742.htm

