Syphilis
Syphilis is bacteria infection that is most often spread through sexual contact.
Causes
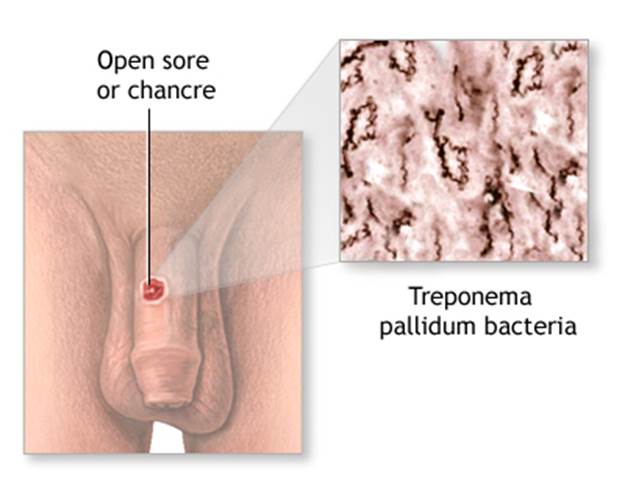
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted, infectious disease caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. This bacterium causes infection when it gets into broken skin or mucus membranes, usually of the genitals. Syphilis is most often transmitted through sexual contact, although it also can be transmitted in other ways.
Syphilis occurs worldwide. Syphilis is more common in urban areas, and the number of cases is rising fastest in men who have sex with men. Young adults ages 15 - 25 are the highest-risk population. People have no natural resistance to syphilis.
Because people may be unaware that they are infected with syphilis, many states require tests for syphilis before marriage. All pregnant women who receive prenatal care should be screened for syphilis to prevent the infection from passing to their newborn (congenital syphilis).
Syphilis has three stages:
- Primary syphilis
- Secondary syphilis
- Tertiary syphilis (the late phase of the illness)
Secondary syphilis, tertiary syphilis, and congenital syphilis are not seen as often in the United States as they were in the past because of the availability of:
- Free, government-sponsored sexually transmitted infection (STI) clinics
- Screening tests for syphilis
- Public education about STIs
- Prenatal screening
Symptoms
Symptoms of primary syphilis are:
- Small, painless open sore or ulcer (called a chancre) on the genitals, mouth, skin, or rectum that heals by itself in 3 - 6 weeks
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the area of the sore
The bacteria continue to grow in the body, but there are few symptoms until the second stage.
Secondary syphilis symptoms may include:
- Skin rash, usually on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- Sores called mucous patches in or around the mouth, vagina, or penis
- Moist, warty patches (called condylomata lata) in the genitals or skin folds
- Fever
- General ill feeling
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Vision changes
- Hair loss
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis depend on which organs have been affected. They vary widely and are difficult to diagnose. Symptoms include:
- Damage to the heart, causing aneurysms or valve disease
- Central nervous system disorders (neurosyphilis)
- Tumors of skin, bones, or liver
Exams and Tests
The doctor or nurse will examine you. Tests that may be done include:
- Examination of fluid from sore
- Echocardiogram, aortic angiogram, and cardiac catheterization to look at the major blood vessels and the heart
- Blood tests to screen for syphillis bacteria (RPR or VDRL)-- if positive, one of the following tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis:
- FTA-ABS (fluorescent treponemal antibody test)
- MHA-TP
- Spinal tap, and examination of spinal fluid
Treatment
Syphilis can be treated with antibiotics, such as penicillin G benzathine, doxycycline, or tetracycline (for patients who are allergic to penicillin). Length of treatment depends on how severe the syphilis is, and factors such as the patient's overall health.
For treating syphilis during pregnancy, penicillin is the drug of choice. Tetracycline cannot be used because it is dangerous to the unborn baby. Erythromycin may not prevent congenital syphilis in the baby. People who are allergic to penicillin should ideally be desensitized to it, and then treated with penicillin.
Several hours after getting treatment for the early stages of syphilis, people may experience Jarish-Herxheimer reaction. This is caused by an immune reaction to the breakdown products of the infection.
Symptoms and signs of this reaction include:
- Chills
- Fever
- General feeling of being ill (malaise)
- Headache
- Joint aches
- Muscle aches
- Nausea
- Rash
These symptoms usually disappear within 24 hours.
Follow-up blood tests must be done at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months to ensure that the infection is gone. Avoid sexual contact when the chancre is present, and use condoms until two follow-up tests have indicated that the infection has been cured.
All sexual partners of the person with syphilis should also be treated. Syphilis is extremely contagious in the primary and secondary stages.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Syphilis can be cured if it is diagnosed early and completely treated.
Secondary syphilis can be cured if it is diagnosed early and treated effectively. Although it usually goes away within weeks, in some cases it may last for up to 1 year. Without treatment, up to one-third of patients will have late complications of syphilis.
Late syphilis may be permanently disabling, and it may lead to death.
Possible Complications
- Cardiovascular complications (aortitis and aneurysms)
- Destructive sores of skin and bones (gummas)
- Neurosyphilis
- Syphilitic myelopathy - a complication that involves muscle weakness and abnormal sensations
- Syphilitic meningitis
In addition, untreated secondary syphilis during pregnancy may spread the disease to the developing baby. This is called congenital syphilis.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if you have symptoms of syphilis.
If you have had intimate contact with a person who has syphilis or any other STI, or have engaged in any high-risk sexual practices, including having multiple or unknown partners or using intravenous drugs, contact your doctor or nurse, or get screened in an STI clinic.
Prevention
If you are sexually active, practice safe sex and always use a condom.
All pregnant women should be screened for syphilis.
Alternative Names
Primary syphilis; Secondary syphilis; Late syphilis; Tertiary syphilis

